synapse
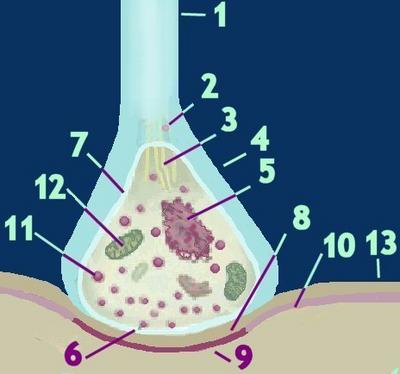
Synaptic vesicles (2) containing neurotransmitters are transported from the cell body (soma) of the pre-synaptic neuron along microtubules (3) within axons and dendrites (1). Synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitter peptides (11) are stored in the terminal button (4).When an incoming action potential reaches the terminal button, neurotransmitter is released from those vesicles (6) adjacent to the pre-synaptic membrane (7) into the synaptic cleft (8).
The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse rapidly across this cleft and interact with the post-synaptic density (9), a modification of the post-synaptic membrane (10) of the post-synaptic neuron (13). The post-synaptic density is rich in CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, a Ca2+/calmodulin-activated dodecameric enzyme, which has the property of self-phosphorylation.
Molecular structures of the commonest neurotransmitters: 5-HT, acetylcholine, dopamine, GABA, glycine, norepinephrine.
Roughly 10 small-molecule transmitters and over 50 recognized neuroactive peptides comprise the commonly recognized neurotransmitters. Fatty acids are candidates for the endogenous canabinoid. Among the small-molecule neurotransmitters are: acetylcholine, 5 amines, and 3 0r 4 amino acids. Serotonin, or 5-HT is a product of the amino acid tryptophan. Aspartate, glutamate, and GABA are also derived from amino acids (aspartic acid, glutamic acid). Glycine is the smallest amino acid. Dopamine is a catecholamine and is a precursor the biosynthetic pathway to the other catecholamine neurotransmitters epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Dopamine is synthesized in the body (predominantly in nervous tissue and adrenal glands) by the decarboxylation of DOPA by the enzyme aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase. Dopamine beta hydroxylase converts dopamine to norepinephrine, and phenylethanoamine N-methyl transferase converts norepinephrine to epinephrine.
The terminal button also contains mitochondria (12), and the cisterna (13). The cisterna is a part of the Golgi apparatus : through the process of pinocytosis, it receives portions of the presynaptic membrane, recycling them into synaptic vesicles.







0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home